Have you ever wondered how many grams of protein per day you should eat for optimal benefits? Or maybe you already eat a lot of protein but want to find out if you’re getting enough? Let’s talk about what proteins are, good sources of protein and how you can use the protein calculator here to figure out a starting point.
What is protein?
Protein is a type of nutrient that the body needs to function properly. They are made up of amino acids that are essential building blocks for muscles, bones, skin, hair and other tissues in our body. Protein is found naturally in many foods, including meat, fish, eggs, milk, beans and nuts.
What does protein do to your body?
Protein is an essential component of every cell in your body. When you eat protein, it is broken down into individual amino acids that are incorporated into the muscles and other tissues of the body.
These are some of the protein’s important functions:
- Muscle repair and growth. The protein in your muscles is normally broken down and rebuilt on a daily basis, and a healthy supply of amino acids is necessary for muscle protein synthesis, the creation of new muscle. Consuming sufficient protein in the diet helps to prevent muscle loss and – when combined with resistance training – promotes muscle growth.
- Maintain healthy skin, hair, nails, bones and internal organs. Although protein turnover in these structures is slower than in muscle tissue, new amino acids are required to replace the old and damaged ones over time. See our related article on retinol for healthy skin.
- Create hormones and enzymes. Many important hormones – including insulin and growth hormone – are also proteins. Similarly, most of the enzymes in our body are proteins. Your body relies on a continuous supply of amino acids to make these vital compounds.
In addition, both clinical experience and scientific studies suggest that getting enough protein can make it easier to control weight. This may be because protein can reduce appetite and prevent overeating by triggering hormones that promote feelings of fullness and satisfaction . Your body also burns more calories when digesting protein compared to fat or carbohydrates.
Finally, there is growing evidence that increased protein intake in a low carbohydrate diet lowers liver fat and blood sugar in the absence of any weight reduction. Protein can also limit the deposition of fat in the liver under conditions such as overeating fructose.
How much protein every day
Considering different views among experts on keto and low-carb diets, we recommend a protein intake of 1.2 to 2.0 grams per kilogram of reference body weight for most people. Protein intake within this range has been shown to preserve muscle mass, improve body composition and provide other health benefits for people eating low-carb or higher carbohydrate diets.
If you are close to your ideal weight or very muscular, use your actual body weight (in kilograms) to calculate your protein requirement in the calculator at the bottom. Otherwise, you can use your height – and the table below – to estimate a quick guide to how much protein you should aim to eat most days based on your height.
Height | Women | Men |
|---|---|---|
Under 163 cm | 90 grams | 105 grams |
163 to 170 cm | 100 grams | 110 grams |
171 to 178 cm | 110 grams | 120 grams |
179 to 188 cm | 120 grams | 130 grams |
Over 188 cm | 130 grams | 140 grams |
Why is protein important for your body?
Protein is an essential building block for your body. Proteins are found in every cell in your body, and the basic structure of protein is a chain of amino acids. Your body needs protein to repair cells and create new ones. Protein is also important for growth and development in children, adolescents and pregnant women.
Protein sources are broken down into amino acids during digestion, and you need a range of amino acids in sufficient quantity to maintain good health. Amino acids are found in animal sources such as meat, milk, fish and eggs, and in plant sources such as soybeans, beans, legumes, nut butters and some grains (such as wheat germ and quinoa).
Amino acids are classified into three groups:
- essentials
- Non-essential
- Conditional
Essential amino acids cannot be produced naturally by your body and must be supplied through the food you eat, while non-essential amino acids are produced by the body from essential amino acids or in the normal breakdown of proteins. Conditional amino acids are necessary in times of illness and stress.
What happens if you don’t get enough protein?
The recommended daily protein intake is a good guide for most healthy people. But eating that amount doesn’t always mean you’re getting what you need.
A perfect example is age. Our bodies don’t use protein as efficiently to build and maintain muscle as we age. If we give a teenager 4 ounces of protein, they will be more efficient at building muscle with that protein than someone who is 50, 60 or older. The recommended amount is really the absolute minimum we need to avoid a shortage situation.
The problem is that you won’t necessarily notice early signs of low protein intake. However, if it continues to be low for a long time, you may see signs of deficiency – which can have serious health effects.
Some signs of protein deficiency include:
- Brittle hair and nails, often the first sign of deficiency
- Feeling of weakness or hunger, as protein provides energy and satisfies appetite
- Frequent diseases without protein to boost the immune system
- Mood swings or difficulty thinking due to fluctuating blood sugar and the protein’s effect on the brain’s neurotransmitters (which regulate mood)
- Muscle weakness, as amino acids are necessary to build muscle mass
- Stress fractures when bone tissue does not have the protein it needs
- If your doctor is concerned, they may perform blood tests for further evaluation. They will use the results along with other information about your health, lifestyle and diet to determine your overall nutritional status.
Which foods are rich in protein?
It’s not always easy to know which foods are high in protein. Read on here for a list and tips and foods that fit into a healthy, high-protein lifestyle adapted for intermittent fasting and low-carb diets.

Foods high in protein and low in carbohydrates
- Eggs are a great source of protein with minimal carbohydrates.
- Tuna is a good source of protein and also contains healthy fatty acids.
- Sardines are rich in protein and omega-3 fatty acids, and very low in carbohydrates.
- Meat, such as beef, chicken or pork, gives you plenty of protein and is naturally free of carbohydrates.
- Fish, such as salmon or trout, is another great source of protein that is also rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Greek yogurt is a healthy source of protein, especially if you choose a low-fat and low-sugar option.
Hope this helps you in your search for foods that are high in protein and low in carbohydrates!
Foods high in protein and low in fat
- Turkey breast: Turkey is an excellent source of protein, and lean turkey breast is especially good if you want to avoid fat.
- Chicken breast: Chicken breast is another great source of protein, and if you remove the skin, then it will have less fat.
- Fish: Fish is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and many fish varieties are also high in protein and low in fat. Try salmon, tuna, cod or saithe.
- Eggs: Eggs are an excellent source of protein and at the same time have minimal fat. They are also versatile and can be prepared in many ways.
- Beans: Beans and other legumes are rich in protein and fiber, and are low in fat. Try kidney beans, lentils or chickpeas.
- Skimmed milk and yogurt: Dairy products such as skimmed milk and yogurt are high in protein and low in fat. Greek yogurt is also a good option.
- Lean meat – Lean meats such as turkey and pork are also good options when you want a low-fat source of protein. Just make sure to avoid processed meat and choose lean cuts.
- Low-fat cottage cheese – Cottage cheese is a good source of protein and low fat for those who can tolerate milk. It’s a versatile food that can be eaten on its own or used in recipes such as smoothies or as a topping.
How much protein in eggs?
Eggs are a good source of natural protein and can be a cheap substitute for other protein sources such as meat. But how many grams of protein are there in eggs? Well, it depends on the size of the egg.
On average, an egg contains between 5.2 and 7.5 grams of protein, depending on its size. To be more specific, a medium egg contains about 6.4 grams of protein, which makes up about 12.6% of the total edible portion.
Protein is found in both the egg white and the yolk, but there is actually a higher concentration of protein in the yolk than in the egg white – but since there is more egg white in the egg, it means that the egg white provides more protein overall.
Business information | Small egg (48 g) | Medium egg (58 g) | Large egg (68 g) | Very large egg (78 g) | Per 100 g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Protein (g) | 5.2 | 6.4 | 7.5 | 8.7 | 12.6 |
Protein sources for vegans and vegetarians
There are many plant-based foods that are rich in protein and can be good sources for vegans and vegetarians. Here are some examples:
- Beans and lentils: These are great sources of protein and can be used in a variety of different dishes, such as stews, salads and veggie burgers.
- Tofu and tempeh: These foods are made from soybeans and are rich in protein. They can be used as a substitute for meat in many dishes.
- Quinoa: This is a gluten-free whole grain that is rich in protein and can be used as a substitute for rice or pasta.
- Nuts and seeds: These foods contain not only protein, but also healthy fatty acids and other nutrients. Try adding nuts and seeds to healthy cereals, smoothies, or use them as a healthy snack.
- Vegetables: Many vegetables actually contain a surprising amount of protein. Try adding spinach, broccoli, bean sprouts, and peas to your diet to increase your protein intake.
- There are many more sources of protein for vegans and vegetarians than this, so it’s worth doing some research and experimenting with different foods to find the ones that work best for you.
How much protein do you need when you exercise?
Proteins are important building blocks in the body, and it’s especially important to make sure you get enough when you exercise. How much protein you need depends on several factors, including the type and intensity of exercise, body weight and your training goals. But according to the mayo clinic, they recommend the following:
Strength training
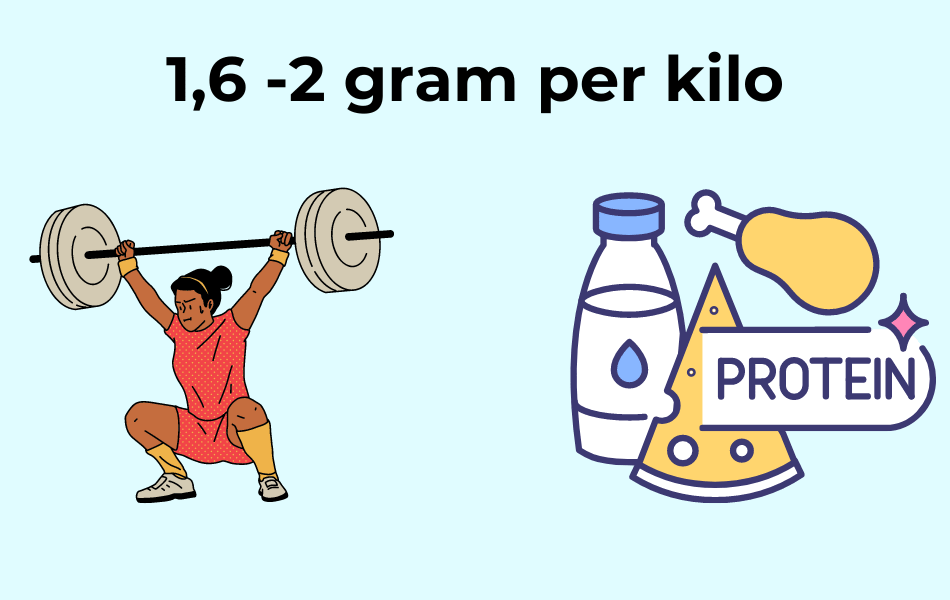
For those involved in strength training, it is recommended that you consume 1.6-2.0 grams of protein per kilo of body weight per day. This is because strength training leads to a breakdown of muscle tissue, and it is important to get enough protein to repair and rebuild muscle tissue. Read the related article and benefits of calisthenics training .
Cardio training

If you’re doing cardio, you won’t need as much protein as when you’re strength training. For those who engage in moderate cardio exercise, it is recommended to consume 1.2-1.4 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. For those who engage in more intense endurance training, such as long-distance running, protein requirements can increase to 1.6-1.8 grams per kilogram of body weight per day.
How can protein help you lose weight?
Protein can help you lose weight in a healthy way. Protein is an essential nutrient that plays an important role in the body’s normal function and health. Studies have found that protein can help keep us fuller for longer, potentially playing a role in successful weight loss.
Here we’ll discuss how protein can help with weight loss, where to get the best sources of protein from your diet, and other tips for losing weight in a sustainable way. A review published in the journal “Frontiers in Endocrinology” shows that diets rich in protein can help us feel fuller for longer, use more energy, build muscle mass and maintain weight loss over longer periods of time.
Protein can help you lose weight because it makes you feel fuller, which can prevent overeating. Furthermore, high protein intake can increase energy expenditure and lead to increased weight loss over time. Another benefit is that the body has a harder time storing protein as fat. Thus, a higher protein diet can lead to less fat storage over time.
Common myths and misconceptions about protein
Protein doesn’t just build muscle
Protein is an essential nutrient that is made up of building blocks known as amino acids. It is not only a component of muscles, but also of bones, joints, tendons, ligaments, hair, antibodies, hormones, enzymes and more. Protein also supports a healthy immune system, and plays a role in body composition
Too much protein leads to kidney disease
Although it has been said that eating too much protein can lead to kidney disease, several studies show that this only applies to people who already have underlying kidney or liver disease. This is because healthy kidneys are good at removing the extra nitrogen that comes with a high intake of protein.
For maximum benefits, don’t worry about when or how you eat protein, just eat enough of it.
People tend to eat most of their protein at lunch and dinner, but to maximize muscle protein synthesis (building muscle mass for a healthy metabolism), research has shown that it’s best to eat about 20 to 30 grams per meal (in addition to a level of carbohydrates and fat appropriate for your diet). If you eat protein at lunch and dinner, consider changing your breakfast to something with Greek yogurt, eggs, veggie burger patties or turkey sausage.
Proteins are converted to sugar
The myth that protein-rich foods and some protein supplements just turn into sugar (glucose, or insulin to be exact) and are a waste of time and money is contrary to good evidence.
Firstly, you need to know that protein from foods and most supplements is digested slowly because the body needs to break it down into ready-to-use amino acids for its many functions. The reality is that research has shown that meals containing 25-40% of total calories help maintain healthy blood sugar levels. This is one of the main reasons why reducing carbohydrates and replacing them with proteins and healthy fats has brought millions of people improved health.

Protein Calculator – How much protein per day
The recommended protein per day from the calculator is just a starting point. You will get a more accurate recommendation if you read the full article and take into account individual differences. It is important to always consult a doctor or other knowledgeable healthcare professional if you have underlying medical conditions, are pregnant or breastfeeding, or are using extreme amounts of protein.
Frequently Asked Questions
Protein requirements depend on the type and intensity of exercise. For most people who exercise moderately to hard, it is recommended to eat 1.2-2 grams of protein per kilo of body weight per day. This contributes to muscle growth and repair after exercise.
If you eat too much protein, it can lead to kidney and liver overload in extreme cases. This can lead to the excretion of minerals and the development of kidney stones. It can also lead to weight gain if you eat more protein than your body needs.
Foods that are rich in protein include meat, fish, poultry, eggs, dairy products, soy products, legumes and nuts.
Protein is essential for building and repairing muscles, bones, skin and organs. Protein also plays a role in producing hormones and enzymes, maintaining a healthy immune system and helping to regulate blood sugar.
Older people need more protein to maintain muscle mass and strength. Protein also helps increase bone health and reduce the risk of injuries and falls.
Protein is needed to build and repair your body. Protein also helps to control hunger and maintain a healthy immune system.
Not getting enough protein can lead to muscle loss, weakened immune system, poor wound healing and fatigue.
An average egg contains between 5.2 and 7.5 grams of protein, depending on its size.
Conclusion
Protein is an important nutrient that is necessary for the body to function. It is recommended that adults consume a certain amount of protein every day, depending on their activity level and other factors. Foods high in protein can be included in a healthy diet, regardless of whether you eat animal or plant-based sources of protein. By including foods high in protein in your diet, you can ensure you get enough of this important nutrient.